Kokonut Seeds Farm at a Glance
Project Specifications
📅 Dates
Start date: July 15, 2024
💰 Forecasted Budget
US$19,982.12 estimated
US$1.58 per square meter
💸 Source of Funding
ReFi on Arbitrum Grants Program
🤑 Revenue Streams
-
Organic Fruits & Vegetables Wholesale
-
Coconuts Wholesale, Derivatives & By-Products
-
Partnerships with Hotels & Restaurants
⚖️ Governance
Kokonut Core Team
🔂 Profit Allocation
-
40% Land Partnership
-
30% Kokonut Guilds
-
20% Kokonut Network
-
10% Kokonut Foundation
🍀 Public Goods Allocation
10% via Kokonut Foundation
Seeds Farm Overview
This farm will help us expand our network and build on our thesis of sustainable natural assets.
The project's objectives include creating job opportunities, enhancing the quality of life for contributors, and establishing a fair mechanism for funding, managing, and developing coconut plantations while maintaining a commitment to environmental preservation.
Multi-Crop Farming
Promoting the adoption of multi-crop agricultural systems is crucial for optimizing resources, improving biodiversity, and increasing sustainability. By diversifying the crops grown in a given area, farmers can take advantage of the complementary relationships between different plant species, reducing the need for synthetic inputs and enhancing the overall health of the ecosystem.
Multi-crop farming encourages the efficient use of land, water, and other natural resources. Different crops have varying nutrient requirements and growth patterns, allowing the land to be utilized more effectively. This approach also helps to mitigate the risks associated with monoculture farming, where a single crop failure can have devastating consequences.
New Opportunities for Local Farmers
The integration of small producers into the organic food supply network for hotels in the southern region contributes to sustainable economic development and improves the quality of life.
-
Train local farmers in organic farming techniques and sustainable practices, ensuring the quality and consistency of the products supplied.
-
Establish strategic partnerships between local farmers and hotels to create an efficient and reliable supply network.
-
Implement financing and support programs for farmers, facilitating access to necessary resources for organic food production.
-
Develop a logistics and distribution system that ensures timely and proper delivery of organic products to hotels.
-
Promote the creation of cooperatives or farmer associations to strengthen the organization and negotiation power of local farmers.
-
Continuously monitor and evaluate the economic and social impact of the project on the farming community, making necessary adjustments to maximize benefits.
-
Promote the adoption of multi-crop agricultural systems to optimize resources, improve biodiversity, and increase sustainability.
-
Launch awareness and promotion campaigns about the benefits of organic foods and the importance of local consumption, actively involving the local community, tourists, and hotels.
Impact Tracking and Measurement
We track and report on the environmental and social impacts of our project using the EBF Framework for Environmental & Social Impact Reports.
Our reports and achieved milestones are published via Karma GAP to ensure EAS compatibility for long-term use and reference within the ReFi and Climate communities
We employ several eco-friendly practices to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance carbon sequestration:
-
Methane (CH4) reduction
-
Using seaweed-based organic fertilizers
-
Collaborating with local farmers to incorporate seaweed in cow feed
-
-
Nitrous oxide (N2O) reduction
-
Using 100% organic, in-house produced fertilizers
-
Implementing manure management strategies
-
Employing cover crops and crop rotation
-
Adopting no-till or reduced tillage practices (syntropic planting)
-
Integrating trees and agroforestry
-
-
Carbon sequestration
-
Implementing regenerative agriculture practices (estimated 0.4-1.2 metric tons of carbon per acre per year)
-
Creating food forests
-
Tracking land productivity and organic produce yield
-
-
Ocean impact
-
Collecting seaweed for fertilizer production
-
Organizing beach cleanups
-
Restoring marine habitats by reducing oceanic trash
This holistic approach minimizes agricultural carbon footprint, promoting soil health, biodiversity, and restoration of marine ecosystems.
Organic Grocery Stores
Supplying organic products to organic grocery stores will play a crucial role in our sustainable project model. We focus on providing organically grown food, free of synthetic chemicals and pesticides, thus guaranteeing healthier and more environmentally friendly products.
Restaurants & Hotels
Our focus on sourcing organic products represents a commitment to quality, sustainability and health. We provide fresh, organically grown ingredients, which enhance the taste and nutrition of dishes, as well as promote more responsible environmental practices. We will sign agreements with restaurant associations and hotel chains to become distributors of organic products.
Eco-Friendly Individuals
We facilitate access to high-quality products that improve personal health and well-being while contributing to the protection of the planet for future generations. We promote the creation of local supply chains to ensure that communities consume organic products.
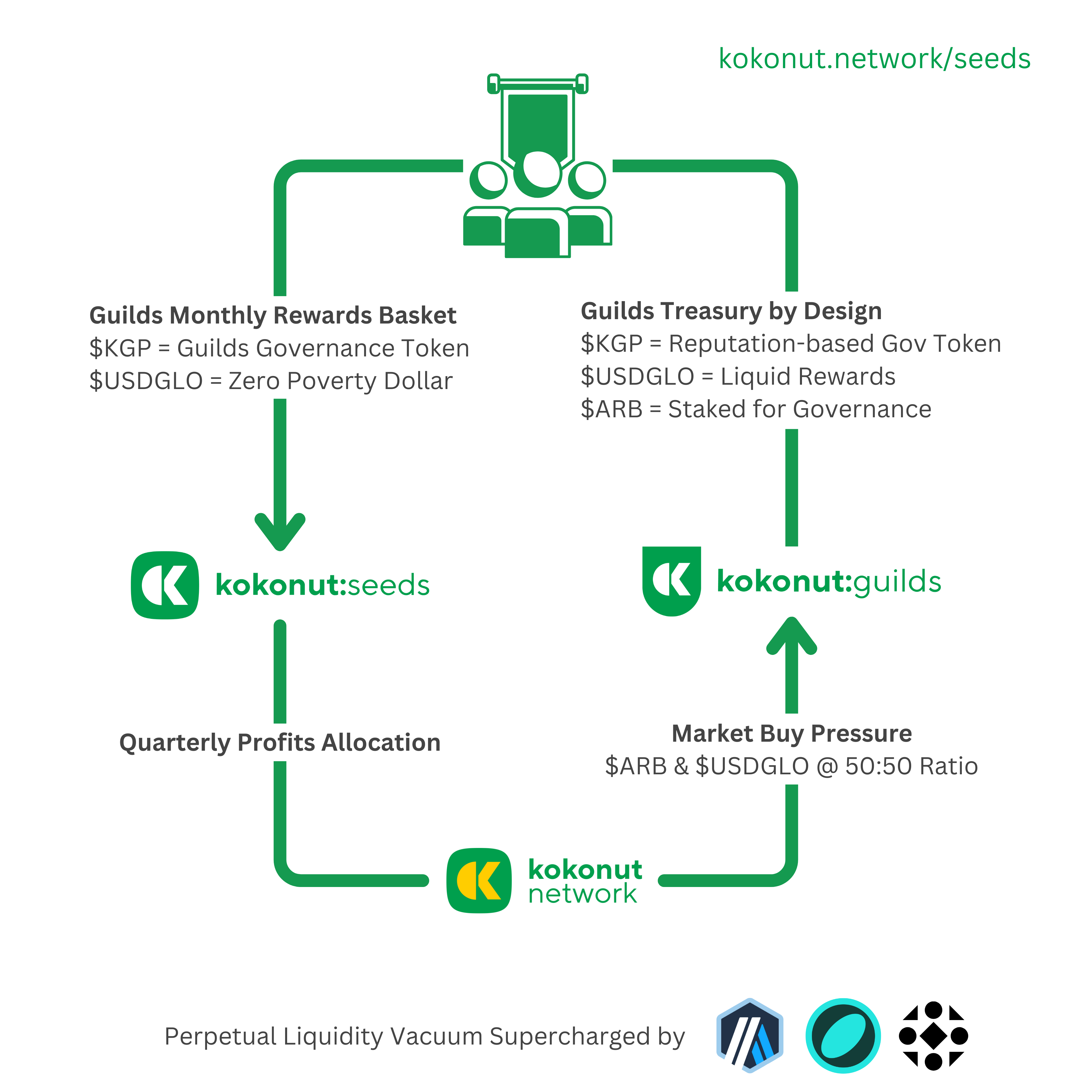
Kokonut Seeds Liquidity Vacuum Mechanism
This flywheel demonstrates how we’re using the Kokonut Framework through our Seeds farm to create a perpetual liquidity vacuum that empowers the Kokonut Guilds.
Kokonut Seeds Crops Gallery
This is a selection of crops for short, medium, and long-term yields, in addition to various trees planted for their ecological benefits.
Sustainable Development Goals
Community-Owned Syntropic Farm and SDGs Alignment